Describe How Independent Assortment During Meiosis Increases Genetic Variation
Spermegg using the equation. The first law responds to the random migration of homologous chromosomes to opposite poles during anaphase I of meiosis both alleles and homologous chromosomes segregate equally or 1.

6 6 Meiosis And Genetic Variation Independent Assortment And Crossing Over During Meiosis Result In Genetic Diversity Ppt Download
During fertilisation 1 gamete from each parent combines to form a zygote.
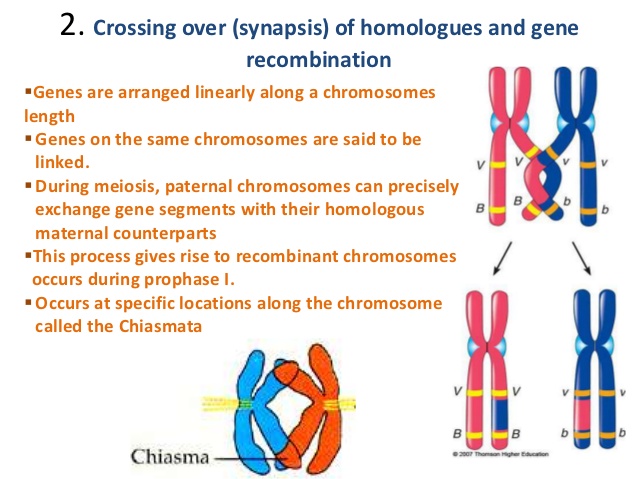
. The homologous chromosomes exchange DNA with each other and assign random chromosomes to two new cells. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote. During meiosis independent eg.
Moreover since it is only half a complement of your chromosomes this leaves room for more genetic diversity when you mate. Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA. Genetic variation is increased by meiosis.
Genetic variation is increased by meiosis. During Meiosis I there are two ways each homologous pairs of chromosomes can line up I I I I - we can calculate the possible number of random combinations of chromosomes in each gamete ie. This variation allows for genetic differentiation in offspring.
Random fertilization of an ovum by a sperm. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote. Random crossing over results in different combinations of genes that may segregate into the gametes.
A gamete will end up with 23 chromosomes after meiosis but independent assortment means that each gamete will have 1 of many different combinations of chromosomes. Recombination or crossing over occurs during prophase I. In meiosis I crossing over during prophase and independent assortment during anaphase creates sets of chromosomes with new combinations of alleles.
This reshuffling of genes into unique combinations increases the genetic variation in a population and explains the variation we see between siblings with the same. The different combinations of chromosomes in daughter cells increases genetic variation between gametes. Not surprisingly the principle of independent assortment applies to the definition of.
The three sources of genetic variability in a sexually reproducing organism are. Genetic variation is also introduced by random fertilization of the gametes produced by meiosis. This answer is correct because the arrangement of chromosomes at the metaphase plate is variable and results in the random distribution of sister chromatids in.
Complete the following statements to describe how independent assortment contributes to genetic variation. In some cases these new combinations may make an organism more or less fit able to survive and reproduce thus providing the raw material for natural selection. Each daughter cell created is genetically half-identical to that of its parent cell yet distinctly different from its parent cell and other daughter cells.
Crossing over between homologous chromosomes during prophase I. It is due to their alignment down the metaphase plate. Genetic variation is increased by meiosis Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA.
1 in gametes and the second law to the random alignment of each pair of homologous chromosomes during. Independent assortment is a genetic term that refers to the variation of chromosomes or genetic information during sex cell division. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote.
During prophase I chromosomes are aligned in pairs mutant alleles and extent generating a tetrad with four chromatids. Genetic variation is increased by meiosis Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA. Hence when you produce gametes your genes are scrambled in each.
There are several points during sexual reproduction at which genetic variation can increase. Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and of nonidentical sister chromatids during meiosis II. Mendels laws reflect chromosomal behavior during meiosis.
Recombination or crossing over occurs during prophase I. B genetic variation increases due to two events crossing over and independent assortment. Click to see full answer.
Recombination or crossing over occurs during prophase IJun 10 2011. This separation is _____. Independent assortment is the production of different combinations of alleles in daughter cells due to the random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator of the spindle during metaphase I.
Crossing over causes different combinations of alleles. Click to see full answer. During Meiosis 1 t he crossing over and independent assortment allow the chromosome to increase the genetic variation.
C Independent assortment further increases genetic variation in gametes because during metaphase 1 the orientation of homologous chromosomes is lined up randomly. During independent assortment _____ chromosomes separate. Genetic variation is increased by meiosis During fertilisation 1 gamete from each parent combines to form a zygote.
The different combinations of chromosomes in daughter cells increases genetic variation between gametes. Describe how independent assortment during meiosis increases genetic variation. The Principle of Independent Assortment.
Independent segregation causes different combinations of maternal and paternal alleles. In this last independent assortment the chromosomes are assigned to four cells. What are two ways meiosis introduces genetic variation.
The Principle of Independent Assortment describes how different genes independently separate from one another when reproductive cells develop. Not all choices will be. In the meiosis 2 there is also an independent assortment.
Meiosis and fertilization create genetic variation by making new combinations of gene variants alleles. Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs during crossing-over which also happens during stage prophase I the exchange of genetic material within non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. Where n is the number of chromosomes in the system.
Number of possible combinations 2n. Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA. Independent assortment is the production of different combinations of alleles in daughter cells due to the random alignment of homologous pairs along the equator of the spindle during metaphase I.
Independent Assortment Definition. A all of the answer describe how genetic variation occurs in meiosis. This produces a unique combination of genes in the resulting zygote.
Genomic diversity and genetic variation is produced through the process of meiosis due to chromosomal recombination and independent assortment. The maternal or paternal homologue may be oriented toward either Question. During meiosis the pairs of homologous chromosome are divided in half to form haploid cells and this separation or assortment of homologous chromosomes is random.
Because of recombination and independent assortment in meiosis each gamete contains a different set of DNA. Explain three ways in which meiosis leads to genetic variation in gametes. The random arrangement of chromosomes during metaphase I creates gametes that are genetically unique from one another.

6 6 Meiosis And Genetic Variation Key Concept Independent Assortment And Crossing Over During Meiosis Result In Genetic Diversity Ppt Download

How Does Meiosis Create Genetic Diversity Socratic
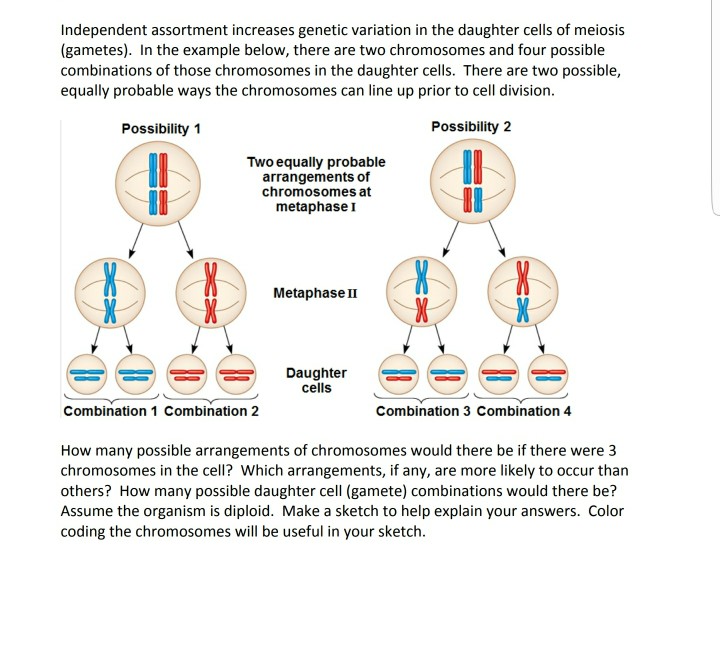
Solved Independent Assortment Increases Genetic Variation In Chegg Com
0 Response to "Describe How Independent Assortment During Meiosis Increases Genetic Variation"
Post a Comment